Hypertrophied Ligamentum Flavum Mri | A multidisciplinary investigation based on clinical, biomechanical, histologic, and biologic assessments. What is ligamentum flavum hypertrophy? The thickness of the ligamentum flavum increases with age and this increase is thought to the most pronounced at the lower lumbar levels 3. The most common spinal disorder in the elderly is lumbar spinal stenosis (lss), which results in part from ligamentum flavum (lf) hypertrophy. This condition affects the yellow ligaments (ligamentum flava) which.
Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy causing cord compression. What are the four imaging modalities. It is a latin word means yellow ligament. Thickening of ligamentum flavum (hypertrophy) can lead to varying degrees of symptoms such as neck pain, back pain, pain radiating down to the arms or legs, numbness, and tingling, inability to stand, walk or lift. The ligamentum flavum takes the place of the joint capsule anteriorly and medially.
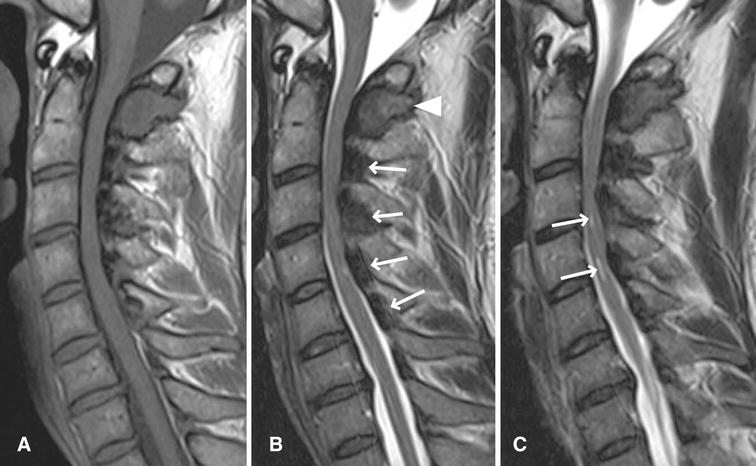
Each ligamentum flavum connects two adjacent vertebrae, beginning with the junction of the axis and third cervical vertebra. Mri evaluation of ligamentum flavum is the only measurable means of evaluations. Pathomechanism of ligamentum flavum hypertrophy: Spinal mri shows hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum causing spinal cord compression. Understanding your mri of the lumbar spine these pictures of this page are about:ligamentum flavum hypertrophy mri. The maximum thickness of the. The section of ligamentum flavum that's hypertrophied or enlarged protrudes into spinal canal and lies against the spinal cord. Hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum is a condition that can lead to paralysis. Some ligaments are on outer side and some others are on ligamentum flavum is like a sheath on inner side of vertebrae. Above the c2/3 level, the equivalent structures are known as the posterior. Although prior histologic and immunochemical studies have been performed in this area, the pathophysiology of loss of elasticity. Assessment of traumatic brain injury online course: Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is a condition in which the ligamentum flavum (lf) thickens due to stresses placed on the spine.
Using imaging data base searching software (primordial, san mateo, california), we searched a chronologic mr imaging data base for all. The maximum thickness of the. Hypertrophy of the ligamentum flavum (lf) is an important contributing factor in lumbar spinal stenosis (lss), lower back pain, as well as sciatica [. Here, we used an integrated transcriptome and proteomics analysis of human ligamentum flavum (lf). pdf radiologic imaging of symptomatic ligamentum flavum thickening with and without.

A multidisciplinary investigation based on clinical, biomechanical, histologic, and biologic assessments. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is also known as ligamentum flavum thickening. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is a condition in which the ligamentum flavum (lf) thickens due to stresses placed on the spine. Thoracic cord compression due to ossified hypertrophied ligamentum flavum. Although prior histologic and immunochemical studies have been performed in this area, the pathophysiology of loss of elasticity. Ligamentum flavum are the ligaments present in spine. Hypertrophy of the ligamentum flavum (hlf) is one of the common causes of lumbar spinal stenosis (lss). Lateral radiograph can show ossified ligaments in some patients. The maximum thickness of the. Beamer yb, garner jt, shelden ch (1973) hypertrophied ligamentum flavum. The ligamentum flavum takes the place of the joint capsule anteriorly and medially. Ct may give a more accurate. Mri evaluation of ligamentum flavum is the only measurable means of evaluations.
Hypertrophy of the ligamentum flavum (lf) is an important contributing factor in lumbar spinal stenosis (lss), lower back pain, as well as sciatica [. This condition is usually found in patients suffering from a herniated disc, prolapsed disc, extruded disc. Lateral radiograph can show ossified ligaments in some patients. This condition involves the ligamentum flava, or aptly named yellow ligament, which is one of the soft tissues inside the spine. Magnetic resonance imaging (mri) was performed to measure the thickness of the lf in each of the 30 patients.
Lateral radiograph can show ossified ligaments in some patients. The thickness of the ligamentum flavum increases with age and this increase is thought to the most pronounced at the lower lumbar levels 3. This ligament attach every upper vertebrae with next lower vertebrae. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy causing cord compression. The key molecules and mechanisms responsible for hlf remain unclear. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is a condition in which the ligamentum flavum (lf) thickens due to stresses placed on the spine. Mri evaluation of ligamentum flavum is the only measurable means of evaluations. Ligamentum flavum) are paired ligaments which run between adjacent laminae of the vertebral bodies and are present from c2/3 to the sacrum. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy soft tissue injuries red bone marrow magnetic resonance imaging nervous system. What is ligamentum flavum hypertrophy? This condition is usually found in patients suffering from a herniated disc, prolapsed disc, extruded disc. He also explained following points in thus video: Introductionas the ligamentum flavum (lf) covers most of the posterolateral part of the lumbar spinal canal, its thickening can be attributed to the development of lumbar canal encroachment.
As discussed, this ligament passes from the anterior and inferior aspect the ossification process appears to be related to degeneration of the elastic fibers, which in the case of ossification of the ligamentum flavum ligamentum flavum hypertrophie. Beamer yb, garner jt, shelden ch (1973) hypertrophied ligamentum flavum.
Hypertrophied Ligamentum Flavum Mri: Using imaging data base searching software (primordial, san mateo, california), we searched a chronologic mr imaging data base for all.
إرسال تعليق